this post was submitted on 21 Jan 2024
39 points (65.4% liked)
Space
8723 readers
4 users here now
Share & discuss informative content on: Astrophysics, Cosmology, Space Exploration, Planetary Science and Astrobiology.
Rules
- Be respectful and inclusive.
- No harassment, hate speech, or trolling.
- Engage in constructive discussions.
- Share relevant content.
- Follow guidelines and moderators' instructions.
- Use appropriate language and tone.
- Report violations.
- Foster a continuous learning environment.
Picture of the Day
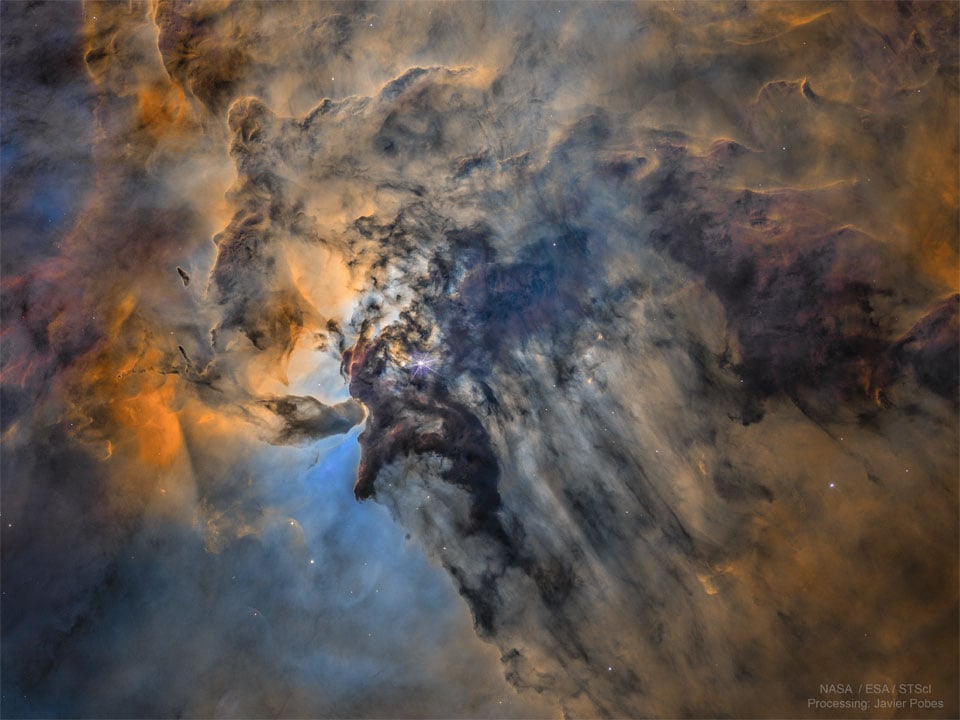 The Busy Center of the Lagoon Nebula
The Busy Center of the Lagoon Nebula
Related Communities
🔭 Science
- !astronomy@mander.xyz
- !curiosityrover@lemmy.world
- !earthscience@mander.xyz
- !esa@feddit.nl
- !nasa@lemmy.world
- !perseverancerover@lemmy.world
- !physics@mander.xyz
- !space@beehaw.org
- !space@lemmy.world
🚀 Engineering
🌌 Art and Photography
Other Cool Links
founded 1 year ago
MODERATORS
you are viewing a single comment's thread
view the rest of the comments
view the rest of the comments

That's true of any galaxies which aren't gravitationally bound. At closer distances (tens/hundreds of millions of light years) gravity wins out over the expansion of space and keeps things together. At larger distances, the expansion of space wins out and clusters of galaxies will drift apart faster and faster until the combined speed of them moving away and us moving away from them will exceed the speed of light and we'll never see those galaxies again.
Our neck of the woods is called the Local Group because scientists are bad at naming things and includes the Milky Way galaxy, and the Andromeda galaxy, as well as between 50 to 80 more galaxies.
As for the black holes, yes, eventually all that will be left are black holes for trillions of years until even those evaporate which is often called the "Heat Death" of the universe. That is just a theory, but if it's true, it won't happen for 1.07x10^106 years. Considering the universe is only 13.8 billion years old right now, that's a very, very, very long time.
Whaaat? Where can I read more of this expansion vs gravity struggle topic?